Everything you need to know Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection of childhood that causes localized clusters of epidermal papules called Mollusca. It mainly affects infants and young children under the age of 10 years. It is more prevalent in warm climates, and in overcrowded environments. Adults are less often infected. Mollusca tend to be more numerous and last longer in children who also have atopic eczema, due to weak skin barrier. It can be very extensive in patients with poor immune function.
What causes molluscum contagiosum?
It is caused by molluscum contagiosum virus.
There are several ways it can spread.
Direct skin-to-skin contact
Indirect contact via shared towels or other items
Auto-inoculation into another site by scratching or shaving
Sexual transmission in adults
Transmission is more likely in wet conditions, such as when children swim together. The incubation period is usually about 2 weeks but can be as long as 6 months.
Clinical features
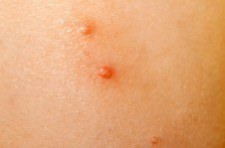
Molluscum contagiosum presents as clusters of small round papules which range in size from 1 to 6 mm, and may be white, pink or brown. Their most striking feature is a central dimple which is a small central pit (this appearance is sometimes described as umbilicated). Each papule contains white cheesy material.
There may be few or hundreds on one individual, commoner in warm moist places, such as the armpit, behind the knees, groin or genital areas. They can arise on the lips or rarely inside the mouth. They do not occur on palms or soles.
When Mollusca are auto inoculated by scratching, the papules often form a row.
Mollusca may induce dermatitis around them, which becomes pink, dry and itchy. As the papules resolve, they may become inflamed, crusted or scabby for a week or two.
Complications of Molluscum contagiosum:
When eyelid is infected it can cause loss of vision. Secondary bacterial infection from scratching .(impetigo)
Disseminated secondary eczema: as an immunological reaction to the virus. Scarring due to surgical treatment
Treatment for molluscum contagiosum?
There is no single perfect treatment of molluscum contagiosum since we are currently unable to kill the virus. Treatments include:
Picking out the soft white core (note, this could lead to autoinoculation)
Cryotherapy by freezing with liquid nitrogen (can leave white marks)
Gentle curettage or electrodessication (can leave a scar)
Laser ablation (can leave a scar)
Molluscum Contagiosum Treatment & Management:
Imiquimod cream - has been reported to be effective in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Cantharidin -, a chemo vesicant that can be used in combination with imiquimod, is effective , test the patient›s response to therapy, treat only a few lesions on the initial visit
Tretinoin - successful in the treatment of small molluscum contagiosum lesions
How can molluscum contagiosum be prevented?
Molluscum contagiosum is infectious while active. However, affected children and adults should continue to attend day care, school and work.
Make every effort not to pass the infection on to others in your family. Stick to your own towel, flannel, clothing and bedding. Keep hands clean Avoid scratching or shaving
Cover all visible lesions with clothing or watertight bandages Dispose of used bandages
However children with molluscum contagiosum need not be kept off school, nor should they be barred from swimming. Infection can be very persistent in the presence of significant immune deficiency.
